Bluetongue, also called bloutong, is more important in sheep. This disease is non-contagious, but is spread by small biting insects (midgets), and is therefore more common in late summer and autumn and can be prevented by vaccination.
It is believed that the virus somehow survives in overwintering midges or animals. Twenty-four serotypes are now recognised in South Africa for this virus, hence the live vaccine divided in three fractions viz. A, B and C, each with a 3-week interval injection. Animals are not to be vaccinated after 8 weeks prior to breeding season, and pregnant ewes are not to be vaccinated at all, because of the fever that is caused by the vaccine. However, if an emergency occur, ewes can be vaccinated in the last half of pregnancy, with risk. Lambs younger than five months are also not to be vaccinated.
Treatment involves nursing:
When outbreaks occur, move animals away from wet areas with standing water where midges flourish.
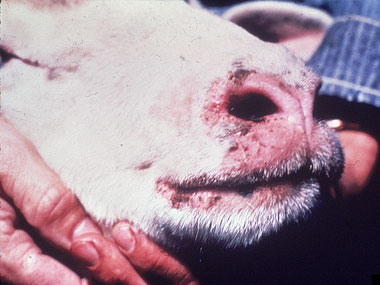
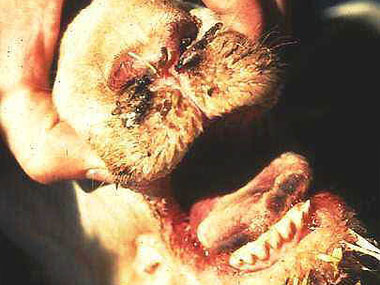
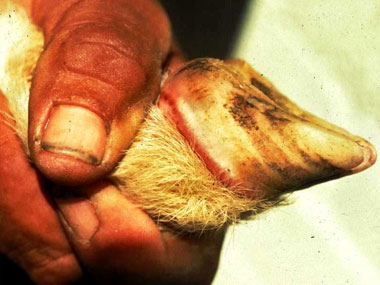
Animals with Bluetongue, have sore muscles and fever, are light sensitive, and are dehydrated. Bluetongue is very similar to flu in people. The fever reaction cause abortions and a break in the wool.
The sheep 's mouth and tongue hurts, and therefore it is to painful for the animal to eat. However, sores in the mouth and a "blue" tongue isn’t always present. Animals do not want to walk because their feet are sore. Sick animals often get secondary pneumonia that can cause death. Well-kept bluetongue cases usually survive.
The treatment of Bluetongue infection is as follows (in order of importance):
The information contained herein is intended only as general guidelines – you should always consult your veterinarian for advice.
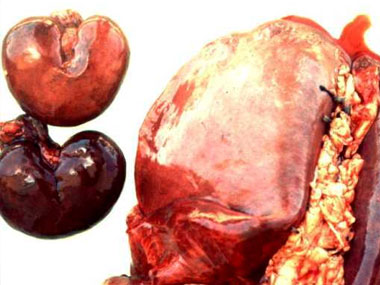
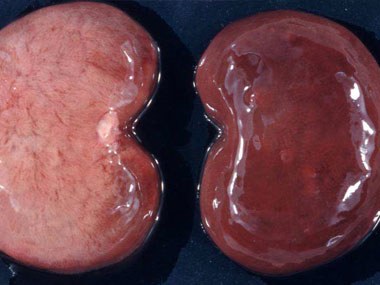
Pulpy kidney is one of the major diseases which the farmer should have knowledge about. The signs seen are usually sudden death and there is usually no time to treat the animals. Sheep die due to toxins released by the overgrowth of Clostridium perfringens type D bacteria normally found in the intestines of sheep. Such overgrowth occurs when sudden changes occur in the diet of the animals and especially accelerate the flow of the intestinal content. One of the names for pulpy kidney is "overeating disease”. (moving sheep to more / better food).
It can also happen when animals, with a heavy precipitation of intestinal parasites are de-wormed. The best prevention is vaccination. Vaccinate animals AT LEAST two times per year.
The information contained herein is intended only as general guidelines – you should always consult your veterinarian for advice
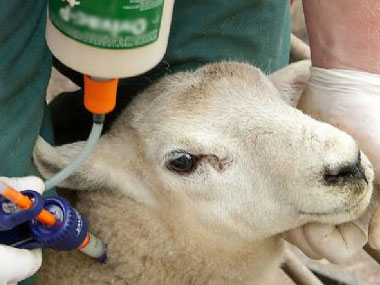
There are many types of worms that can affect sheep, but the most important type is wireworms. The signs seen are often bottlejaw and paleness of the mucous membrane and gums because of the adult worm that cause anemia. Sometimes diarrhea is also noted. Weight loss, loss of appetite and death can occur.
The Famacha© method of selective treatment was developed by three South African researchers (Doctors Faffa Malan, Gareth Bath and Jan van Wyk) as a possible solution for the large anthelmintic resistance problem in South Africa. Since then, the method was successfully implemented worldwide.
The main purpose of the method is to sufficiently maintain susceptible wireworm population (`refugia’) on the pasture. By deworming only those sheep that really needs to be dewormed, resistance to anthelmintics can be delayed. At the same time the farmer monitors the animals and cull those with poor naturally resistant to these worms.
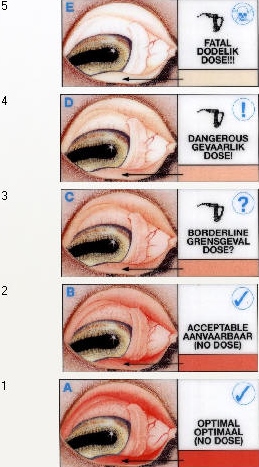
Anemia (as observed in the mucous membrane) can be seen with the help of a color guided card: sheep with a score of 1 has a pink - red mucous membrane color and do not need treatment for wireworm, while those with a score of five has a white mucous membrane and must be dosed immediately against wireworm and probably must be given intensive medical treatment.
The information contained herein is intended only as general guidelines – you should always consult your veterinarian for advice.
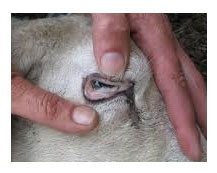

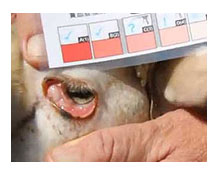
The FAMACHA-chart is available from your local veterinarian who can order it from me. Lana Botha at the Faculty Veterinary Sciences, University of Pretoria. (lana.botha@up.ac.za)